Thyroid And Its Effects
THYROID
Writer: Dr. Ritesh Agrawal, MBBS, MS, MCh, FAIS, Thyroid and Endocrine Surgeon.
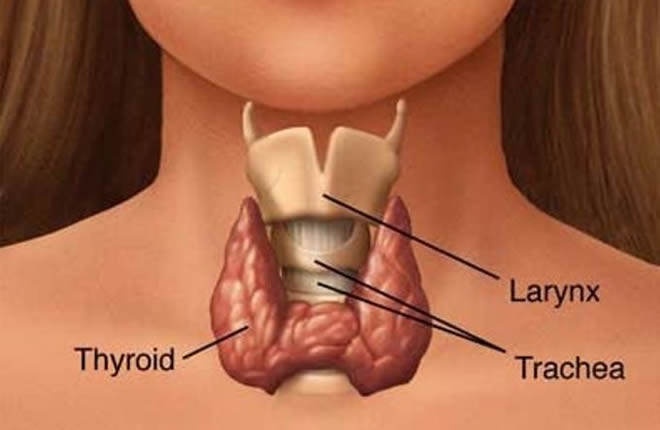
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in your neck. It releases Thyroxine hormone that control metabolism- the way your body uses energy. This hormone regulates vital body functions, including:
Heart rate
Central and peripheral nervous systems
Mood changes
Digestion
Body weight
Muscle and bone strength
Menstrual cycles
Fertility
Body temperature
Cholesterol levels
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism means that the thyroid gland is not making enough thyroxine hormone to keep the body running normally.
Common causes of this hypothyroidism are autoimmune disease, surgical removal of the thyroid, and radiation/ radioiodine treatment.
What are the symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
When thyroid hormone levels are too low, the body’s cells don’t get enough thyroid hormone and the body’s processes start slowing down. As the body slows, the patient may notice a feeling of cold, easy tiredness, dry skin, memory loss and forgetfulness, depression, dullness, constipation, period problems especially heavy bleeding and fertility problems. Because the symptoms are so variable and non-specific, the only way to know for sure whether you have hypothyroidism is with a simple blood test for T3, T4 and TSH.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism means excess amount of thyroid hormones circulating in the body. This is most commonly due to an overactive thyroid gland or swelling of the thyroid gland. Increased levels of thyroid hormones accelerate your body’s metabolism and can lead to different manifestations.
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism could be- sudden weight loss inspite of good appetite, rapid heartbeat or pounding of your heart (palpitations), feeling nervous and irritable, having trouble concentrating, feeling too warm even when other people don’t feel warm, diarrhea, having trouble sleeping, an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter).
Again, the only way to know for sure whether you have hyperthyroidism is with a simple blood test for T3, T4 and TSH.
Thyroid and Growth
Thyroid has an enormously important job to do, especially for teens. Thyroid hormones help to control the growth and the structure of bones, sexual development (puberty), and many other body functions. These hormones are important in determining if your body will mature as it should.
Thyroid hormones also directly affect how most of your organs function. So if your thyroid isn’t operating properly, you can have problems in lots of other parts of your body.
Thyroid and Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time where the smallest deviation from the norm evokes great fear and confusion in a mother ‘s mind.
Thyroid diseases are common in pregnancy because of many changes in the mother’s body to accommodate the newcomer.
The most common problems faced are either a high TSH or a low TSH.
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) is a signal from the master gland in the brain that tells us that there is a change in the quantity of thyroid hormones circulating in the body.
High TSH signifies lower thyroid hormone concentration than required and requires replenishment of the hormone to normalise the TSH, so high TSH means- give me more.
Low TSH is a little more tricky, it means there is a little more thyroid hormone circulating in the mother’s blood.
But this does not mean it is necessarily harmful. Gestational thyrotoxciosis or pregnancy associated thyroid hormone excess is the usual cause and does not require any treatment.
Thyroid and weight
Since the BMR in patients with hyperthyroidism is elevated, many patients with an overactive thyroid do, indeed, experience some weight loss despite a good appetite. On the contrary, in hypothyroid patients, BMR is decreased. Hence an underactive thyroid is generally associated with some weight gain.
Goiter
The term “Goiter” simply refers to an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. It is important to know that the presence of a goiter does not necessarily mean that the thyroid gland is malfunctioning. A goiter can occur in a gland that is producing too much hormone (hyperthyroidism), too little hormone (hypothyroidism), or the correct amount of hormone (euthyroidism). A goiter indicates there is a condition present which is causing the thyroid gland to grow abnormally in size. Some important causes of goiter are- iodine deficiency, thyroiditis (an autoimmune disease or inflammation of thyroid gland), thyroid tumors or cancers. Hence a proper evaluation of any goiter is necessary not to miss a cancer inside thyroid.